Any American who has ever created a new account password while seeking a government service has used some part of the NIST cybersecurity standards, guidelines, or framework. Due to the explosion of mobile device usage, IoT, cloud services, and BYOD, the cybersecurity landscape has changed radically.
Information parameters are extinct. Critical data is present all over the internet. Consequently, hackers and malicious actors are having a field day using modern technologies to gain access and profit from unsecured data.
According to Statista, there has been a sudden increase in data breaches targeting small businesses and non-governmental institutions over the past two decades. Statistics show that over 1,000 breaches in 2020 resulted in the exposure of over 155.8 million sensitive records.
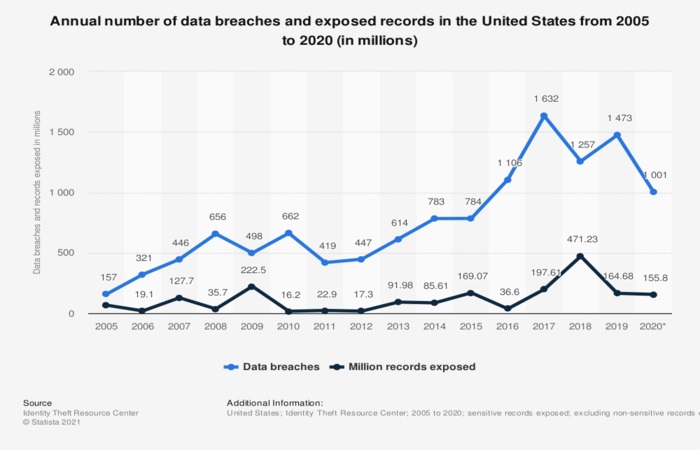
The precariousness of cybersecurity in the world necessitated formal plans to mitigate risks and protect organizations’ valuable assets. Therefore, NIST sets standards that businesses and organizations follow to analyze and improve their computer and data security.
What is NIST?
NIST, which stands for National Institute of Standards and Technology, was founded in 1901 as a non-regulatory agency to set standards and measurements of electronic devices and instruments. It now functions as a part of the US Department of Commerce, and cybersecurity is just one of its functional arms.
NIST is most famous today for offering a voluntary but trustworthy tool that assesses and reduces cyber threats and improves information and IT infrastructure protection. NIST helps organizations ensure their cybersecurity measures meet the minimum standards and is easily implementable.
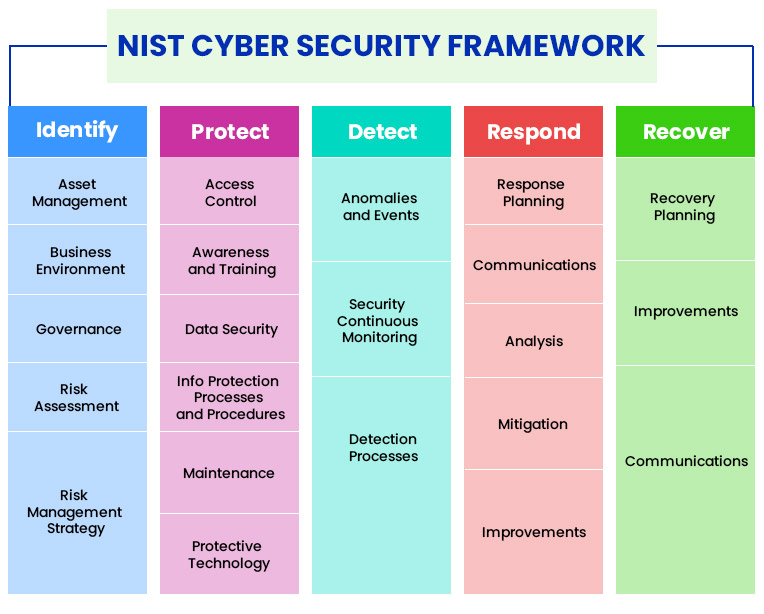
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework
In early 2013, NIST convened a meeting with stakeholders in the computer security industry to develop a cybersecurity framework that addresses current and emerging threats faced by businesses. A year later, in February 2014, the first version of the NIST cybersecurity framework was released. In short, the Cybersecurity Framework combined security best practices with industry safety standards that organizations can use to manage cybersecurity risks.
NIST’s cybersecurity framework was initially formulated with operators and owners of critical infrastructure in the private sector. Gradually, however, its user base grew to include businesses, organizations, and communities worldwide.
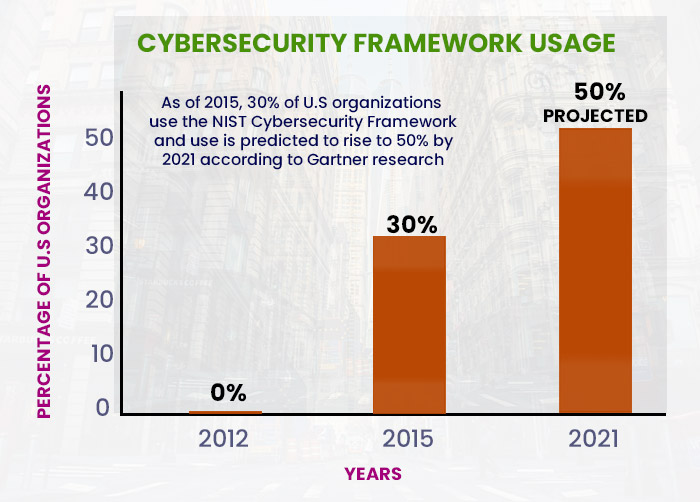
According to Gartner, as many as 50% of American organizations have adopted the NIST cybersecurity framework. It is also becoming increasingly popular outside the United States as it is the best choice for eliminating confusion and conflicting expectations, and duplication of efforts in cybersecurity.
The Main Objectives of the NIST Compliance
NIST’s cybersecurity framework fulfills the need for the world to have standardized cybersecurity procedures, policies, and standards, especially for critical infrastructure. The objectives that the NIST cybersecurity framework compliance fulfills include:
- Helping businesses and organizations identify, assess, and manage threats to their critical infrastructure.
- Helping essential infrastructure sectors with neutral guidance to leverage the latest technologies to become more competitive in the market.
- Setting the standard for measuring the effectiveness of implemented cybersecurity measures.
- Determining the security standards and guidelines that can apply to every sector of critical infrastructure.
Above all, the NIST cybersecurity framework created a prioritized and flexible approach to security. Small businesses and organizations found it easier to adopt the performance-based and repeatable system for data and infrastructure protection as it is cost-effective.
How an Organization Can Gain NIST Compliance?
With assistance from a professional IT consultant or managed security service provider, your organization can set up security that complies with the NIST standards of cybersecurity.
Organizations can implement the NIST cybersecurity framework in four tiers. They are Partial, Risk-informed, Repeatable, and Adaptive (1 to 4) tiers.
The right tier for an organization depends on its security objectives and requirements. For instance, if your organization has a higher risk appetite and has the resources to invest in cybersecurity, the fourth tier (Adaptive) would be the ideal cybersecurity implementation.
The most common standards organizations can choose from are:
1) NIST FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standards) for contractors, government agencies, and vendors. It is used to manage encryption algorithms and data.
2) NIST Special Publication 800-37 promotes continuous monitoring of information security controls to manage risks.
3) NIST Special Publication 800-53 analyzes compliance by subcontractors working in a federal supply chain.
4) NIST Special Publication 800-171 is used by organizations and non-federal systems handling unclassified information.
Organizations that meet the NIST compliance requirements can self-certify their security standards since NIST does not issue official certifications. Since compliance is an ongoing process, organizations must commit to maintaining the cybersecurity standards specified in their compliance contract.
Also Read: Cybersecurity Solutions Provider
Does Your Organization Need NIST Compliance?
NIST does a lot more than managing a cybersecurity framework; it also lays the foundation for organizations looking to comply with other regulations such as FISMA and HIPAA. Their framework is comprehensive and would benefit any business or organization with information to secure.
More Articles:
- President Biden Strengthen US Cybersecurity!
- 83% Of Large-scale Enterprises Transformed Their Cybersecurity!
- Mobile Cybersecurity Threats to Protect Your Data!
- Cybersecurity Myths and Misconceptions Worth Knowing!
- How Businesses Can Implement ‘Zero Trust Security’?
- Cybersecurity Trends in 2021 and Beyond!
- How To Create An Information Security Program Plan?

