Cybersecurity Insider threats have become a major concern in the increasingly interconnected digital world. Whether intentional or accidental, statistics show that the impact of the insider threat on the business remains the same.
Insider threats are particularly devastating because of the knowledge, access, and information possessed by the insiders, which can lead to a catastrophic loss to the company following an insider breach.
Increasing volumes of unstructured data and the availability of information-sharing tools make it easier for employees to cross the company policy and carry out malicious activities.
Egress’s recent 2020 Insider Data Breach Survey sheds light on the growing occurrence of insider data breaches in the last 12 months.
According to the report, 97% of the surveyed IT leaders expressed concerns about the risk of insider data breaches, up by 2% from 2019.
Among the IT leaders,
- 78% expressed that employees caused data breaches accidentally
- 75% revealed that employees caused data breaches intentionally
Among the surveyed employees,
- 71% agreed they have intentionally shared company information externally
- 68% said they have accidentally shared information
While the percentage of IT leaders who believe employees have inadvertently caused data breaches remained the same since 2019, the portion who think employees have deliberately put data at risk has increased by 14%.
Causes of Insider Data Breaches

The cybersecurity vulnerabilities have increased as employees have become ultra-mobile and the workplace has become less defined.
Moreover, the coronavirus pandemic has made remote work a new normal. As employees started working outside the company, especially in their home environment, there’s a growing risk that they could develop a more proprietary attitude to the data they access/handle.
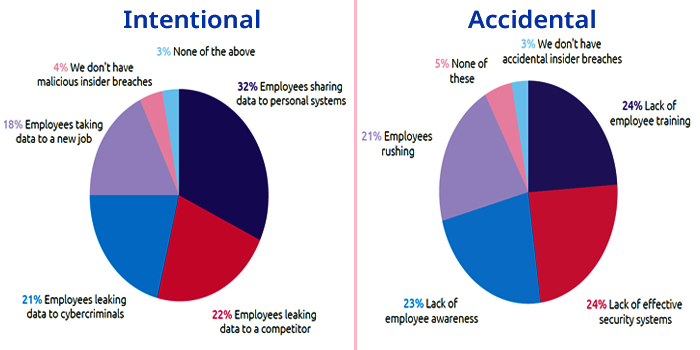
Causes of Data Breaches, According to IT Leaders

Causes of Intentional Insider Breaches
- 32% of Employees share data with personal systems
- 22% of Employees leak data to a competitor
- 21% of Employees leak data to cybercriminals
- 18% of Employees take information on a new job
Causes of Accidental Insider Breaches
- 24% Lack of employee training
- 24% Lack of adequate security systems
- 23% Lack of employee awareness
- 21% of Employees rushing
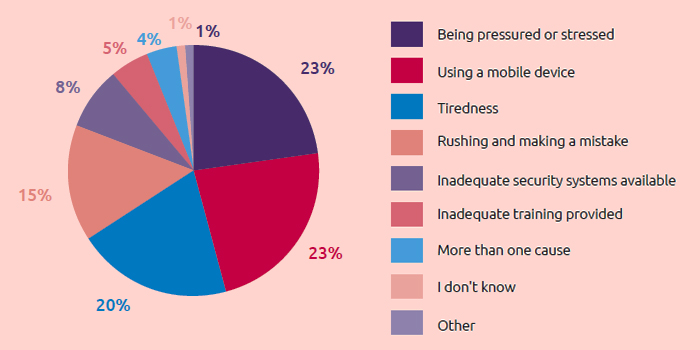
Causes of Data Breaches, According to Employees
- 23% Being pressured or stressed
- 23% Using a mobile device
- 20% Tiredness
- 15% Rushing and making a mistake
- 8% Inadequate security systems available
- 5% Inadequate employee training
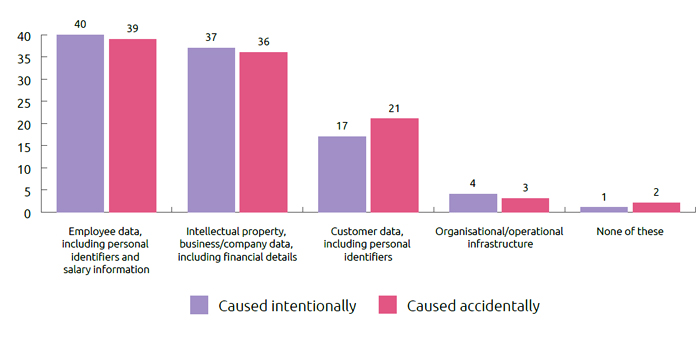
What Data is Most Vulnerable to Insider Data Breach?
According to the report, employee data, including personal identifiers and salary information, is most at risk for both accidental and intentional internal data breaches.
Intentional Data Breach:
| Impact of Insider Breaches | Intentional Data Breach |
| Employee Data | 40% |
| Company Data | 37% |
| Customer Data | 17% |
| Organizational/Operational Infrastructure | 4% |
Accidental Data Breach:
| Impact of Insider Breaches | Accidental Data Breach |
| Employee Data | 39% |
| Company Data | 36% |
| Customer Data | 21% |
| Organizational/Operational Infrastructure | 3% |
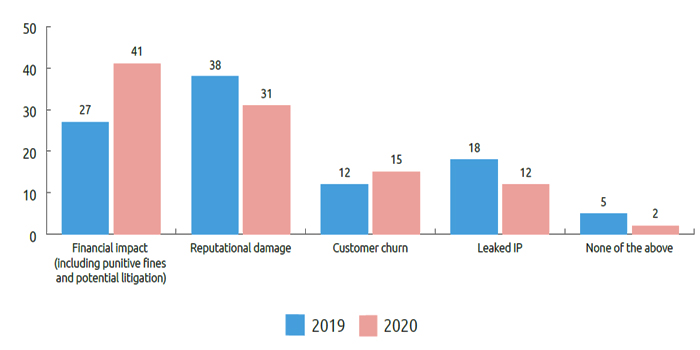
Impact of Internal Data Breaches

According to the report, 41% of IT leaders expressed that financial damage is the area of the significant impact of the internal data breach, up from 27% in 2019.
Moreover, the concern about financial impact is highest in the US, with 43% saying it is the area of most significant concern.
The increase in financial losses due to an internal data breach is mainly due to the introduction and enforcement of stringent data privacy regulations in recent years.
The recently implemented GDPR and CCPA laws press unprecedented penalties for companies that fail to comply with the new regulations.
| Impact of Insider Breaches | IT Leaders Who Replied Positively |
| Financial Impact | 41% |
| Reputational Damage | 31% |
| Customer Churn | 15% |
| Leaked IP | 12% |
Internal attacks can cause catastrophic damage as insiders typically have authorized access to an organization’s critical assets, regardless of whether they have malicious intentions or not.
Cybersecurity Insider Threat Statistics (Infographic)
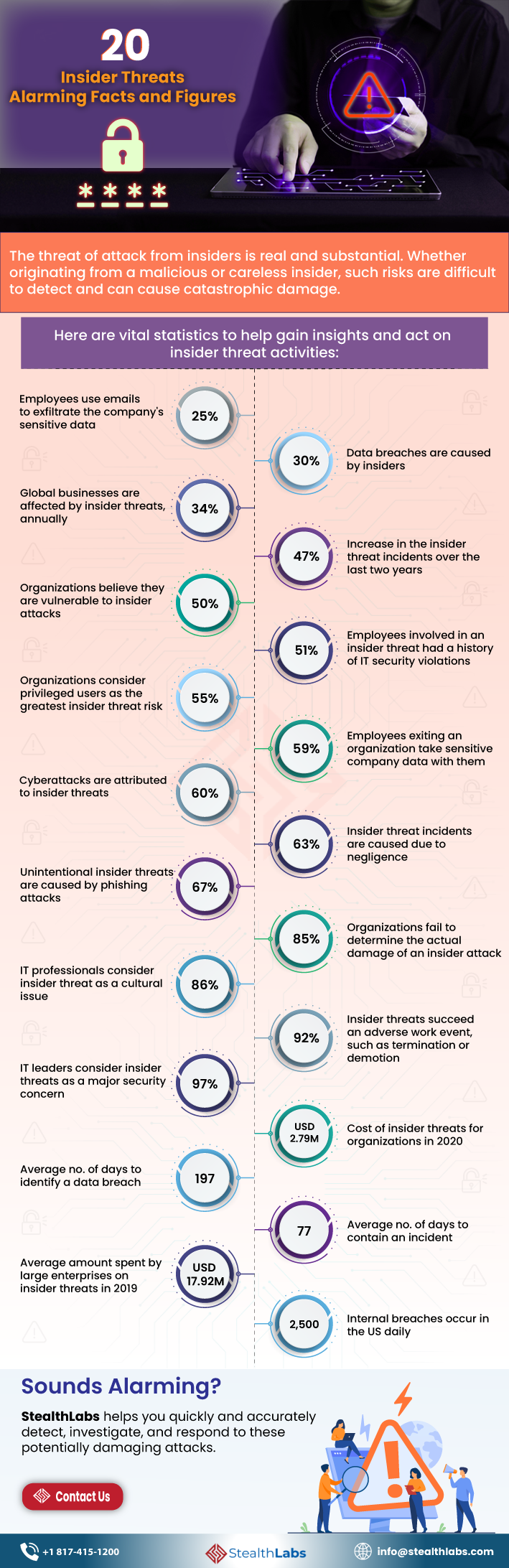
Cybersecurity Insider Threat Statistics: 20 Alarming Facts and Figures
The threat of attack from insiders is real and substantial.
Whether originating from a malicious or careless insider, such risks are difficult to detect and can cause catastrophic damage.
1) 25% of employees use emails to exfiltrate the company’s sensitive data
2) 30% of data breaches are caused by insiders
3) 34% of global businesses are affected by insider threats, annually
4) 47% increase in the insider threat incidents over the last two years
5) 50% of organizations believe they are vulnerable to insider attacks
6) 51% of employees involved in an insider threat had a history of IT security violations
7) 55% of organizations consider privileged users as the greatest insider threat risk
8) 59% of employees exiting an organization take sensitive company data with them
9) 60% of cyberattacks are attributed to insider threats
10) 63% of insider threat incidents are caused due to negligence
11) 67% of unintentional insider threats are caused by phishing attacks
12) 85% of organizations fail to determine the actual damage of an insider attack
13) 86% of IT professionals consider insider threat as a cultural issue
14) 92% of insider threats succeed in an adverse work event, such as termination or demotion
15) 97% of IT leaders consider insider threats as a major security concern
16) USD 2.79M – Cost of insider threats for organizations in 2020
17) 197 – Average no. of days to identify a data breach
18) 77 days – Average no. of days to contain an incident
19) USD 17.92M– Average amount spent by large enterprises on insider threats in 2019
20) 2,500 internal breaches occur in the US daily
In Conclusion
One thing is for sure: Insider breaches continue to be a threat for all organizations, and the future won’t be any different in this regard.
The IT leaders must re-examine their approach and build a technology stack and security strategies that can respond dynamically to employees’ changing behaviors.
Moreover, the organizations should evolve to gain greater visibility of insider breach risk vectors rather than relying on their employees to alert them to a breach.
Let’s Talk!
More Articles:

